Impact of Prostate Cancer: Men over age 50 should be checked periodically.
One common condition that men over the age of 50 should be checked periodically for is prostate cancer. This condition poses significant health risks for older men, making awareness and early detection crucial. Below, I will discuss the importance of prostate cancer screening, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and the role of healthcare providers.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
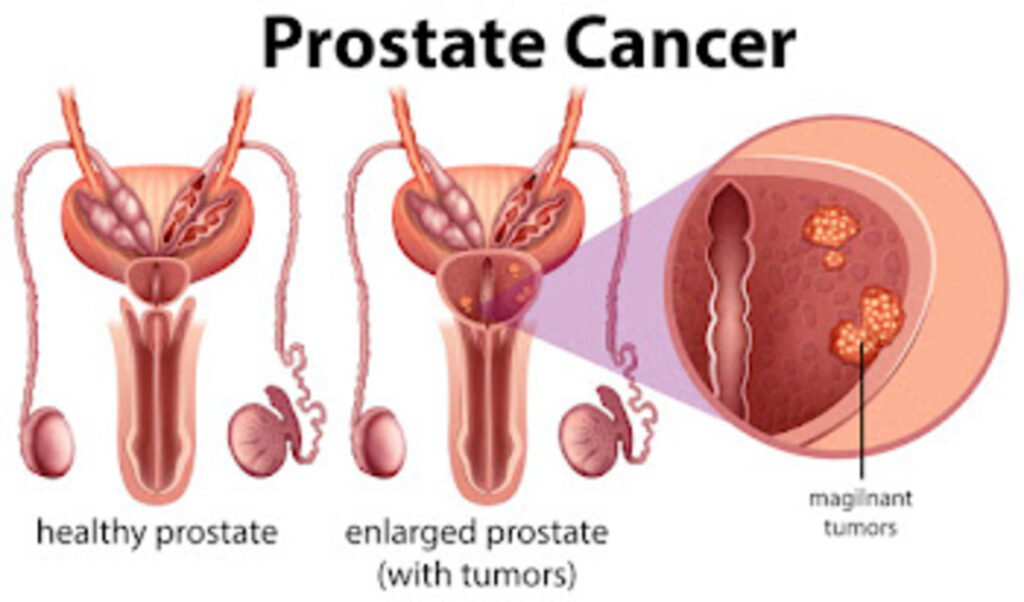
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow uncontrollably. The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum, responsible for producing seminal fluid. While prostate cancer can develop in younger men, the risk significantly increases with age, particularly after 50.
Importance of Screening
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men, with a substantial number of new cases diagnosed each year. Early-stage prostate cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms, which is why screening is vital. Periodic screenings can lead to earlier detection, potentially improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the likelihood of developing prostate cancer, including:
- Age: The risk increases significantly after age 50.
- Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk. If a father or brother had the disease, the risk can double.
- Race/Ethnicity: African American men have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more likely to die from it compared to men of other races.
- Diet: A diet high in red meat and dairy products and low in fruits and vegetables may increase risk.
- Obesity: Obese men are more likely to develop aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
Symptoms
In the early stages, prostate cancer may not present any symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, some common symptoms may include:
- Difficulty urinating or changes in urinary habits
- Blood in urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Persistent pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
These symptoms can also be associated with benign conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which underscores the importance of regular screenings and consultations with healthcare providers.
Diagnostic Methods
Several methods are used to diagnose prostate cancer, including:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): In this exam, a healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel for abnormalities in the prostate.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a substance produced by the prostate. Elevated levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer or other prostate conditions.
- Biopsy: If abnormalities are detected through DRE or PSA testing, a biopsy may be performed. This involves taking small samples of prostate tissue to be examined for cancer cells.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans may be used to determine the extent of cancer if diagnosed.
Treatment Options
Impact of Prostate Cancer If diagnosed with prostate cancer, several treatment options are available, depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the disease:
- Active Surveillance: For low-risk cases, doctors may recommend monitoring the cancer closely without immediate treatment.
- Surgery: A radical prostatectomy involves removing the prostate gland and some surrounding tissue. This option is often considered for localized cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It can be delivered externally or internally (brachytherapy).
- Hormone Therapy: This treatment reduces levels of male hormones that fuel cancer growth. It may be used for advanced cancer or in conjunction with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: In cases where cancer has spread beyond the prostate, chemotherapy may be recommended to target cancer cells throughout the body.
- Immunotherapy: This newer approach uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It may be an option for advanced prostate cancer.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating men about prostate cancer and the importance of screenings. Regular consultations should involve:
- Assessing individual risk factors
- Discussing the benefits and risks of PSA testing and DRE
- Creating a personalized screening schedule based on age and risk factors
Screening Recommendations
Current guidelines suggest that men begin discussing prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers at age 50, or earlier for those with higher risk factors. The decision to undergo testing should be made collaboratively, considering personal preferences, health status, and understanding of potential outcomes.
Latest information Impact of Prostate Cancer
It research and treatment continue to evolve rapidly. Here are some of the latest developments and information regarding impact of prostate cancer:
1. Screening Guidelines
Recent guidelines suggest that shared decision-making is essential when it comes to it screening. Men aged 55 to 69 are encouraged to discuss the potential benefits and risks of PSA testing with their healthcare providers. For high-risk groups (e.g., African American men or those with a family history), discussions may begin as early as age 45.
2. Advancements in Diagnostics
- Genomic Testing: Tests like Oncotype DX and Decipher are now being used to assess the risk of recurrence in prostate cancer patients, allowing for more personalized treatment plans.
- Multiparametric MRI: This imaging technique is increasingly used for better visualization of the prostate and detection of tumors, improving the accuracy of biopsies.
3. Treatment Innovations
- Focal Therapy: Techniques such as high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) and cryotherapy are being explored as less invasive options for localized prostate cancer, targeting only the tumor while sparing healthy tissue.
- Immunotherapy: Treatments like sipuleucel-T (Provenge) are approved for advanced prostate cancer and aim to stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells.
- PARP Inhibitors: Drugs like olaparib are showing promise in treating prostate cancer with specific genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA mutations).
4. Hormonal Therapies
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) remains a cornerstone for advanced prostate cancer, but research into combining ADT with other treatments (like radiation) is ongoing. Newer hormonal therapies, such as enzalutamide and abiraterone, continue to improve outcomes for patients with advanced disease.
5. Active Surveillance
For low-risk prostate cancer, active surveillance remains a preferred approach for many clinicians, allowing patients to avoid the side effects of immediate treatment while closely monitoring the cancer’s progression.
6. Quality of Life Research
Ongoing studies emphasize the importance of quality of life in it treatment, focusing on managing side effects and preserving sexual function and urinary health.
7. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is being increasingly integrated into prostate cancer diagnostics and treatment planning. Machine learning algorithms are being developed to predict outcomes based on various clinical parameters, helping tailor more effective treatment strategies.
8. Patient Education and Support
Increasing emphasis is being placed on patient education regarding the disease, treatment options, and side effects. Support networks and counseling services are also becoming integral parts of comprehensive care.
Above are major Impact of Prostate Cancer.
Conclusion
Impact of Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer management is becoming more personalized, with advancements in diagnostics, treatment options, and patient support. Staying informed about the latest research and guidelines is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike, as this knowledge can significantly influence treatment outcomes and quality of life. Regular discussions with healthcare professionals remain essential for making informed decisions regarding screening and treatment.
It is a significant health concern for men over 50, necessitating regular screenings and discussions with healthcare providers. Early detection is key to successful treatment and improved outcomes. By being informed and proactive about their health, men can take crucial steps in managing their risk for prostate cancer. Regular check-ups, awareness of symptoms, and understanding the available diagnostic and treatment options empower men to make informed decisions regarding their health.